This page offers you a customisable sine wave generator. Below is a generic VHDL description of a sine wave generator. It is parameterised by constants and subtypes declared in sine_package.
Further below is a HTML form for you to specify word and address sizes for a lookup table to store the values of a sine wave. Submit the form and a short Perl script runs on this server to generate a customised sine_package complete with lookup table for you.
This implementation is moderately memory efficient because it stores only the first Pi/2 radians of sine values. The second Pi/2 radians is a mirror image of the first in time and the second Pi radians is a mirror image in amplitude of the first Pi radians.
Memory could be saved if the increments were recorded rather than each absolute value. Fewer bits per value would be needed, however, extra hardware would be needed for an adder.
-- Synthesisable design for a sine wave generator
-- Copyright Doulos Ltd
-- SD, 07 Aug 2003
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
use work.sine_package.all;
entity sine_wave is
port( clock, reset, enable: in std_logic;
wave_out: out sine_vector_type);
end;
architecture arch1 of sine_wave is
type state_type is ( counting_up, change_down, counting_down, change_up );
signal state, next_state: state_type;
signal table_index: table_index_type;
signal positive_cycle: boolean;
begin
process( clock, reset )
begin
if reset = '1' then
state <= counting_up;
elsif rising_edge( clock ) then
if enable = '1' then
state <= next_state;
end if;
end if;
end process;
process( state, table_index )
begin
next_state <= state;
case state is
when counting_up =>
if table_index = max_table_index then
next_state <= change_down;
end if;
when change_down =>
next_state <= counting_down;
when counting_down =>
if table_index = 0 then
next_state <= change_up;
end if;
when others => -- change_up
next_state <= counting_up;
end case;
end process;
process( clock, reset )
begin
if reset = '1' then
table_index <= 0;
positive_cycle <= true;
elsif rising_edge( clock ) then
if enable = '1' then
case next_state is
when counting_up =>
table_index <= table_index + 1;
when counting_down =>
table_index <= table_index - 1;
when change_up =>
positive_cycle <= not positive_cycle;
when others =>
-- nothing to do
end case;
end if;
end if;
end process;
process( table_index, positive_cycle )
variable table_value: table_value_type;
begin
table_value := get_table_value( table_index );
if positive_cycle then
wave_out <= std_logic_vector(to_signed(table_value,sine_vector_type'length));
else
wave_out <= std_logic_vector(to_signed(-table_value,sine_vector_type'length));
end if;
end process;
end;
Lookup Table
We will use a short Perl script to generate a lookup table in a package, sine_package. Specify a word size and address size suitable for your application. Values of 8 and 7 will generate a ROM of size 256 bytes.
Lookup table word size
Lookup table address size
Test Bench
Download an example sine wave generator with a test bench: sine_testbench.zip
We have bundled a simple testbench to show how this code works. There's also a Tcl script called go.tcl to drive ModelSim for you. Here's what the output looks like in ModelSim.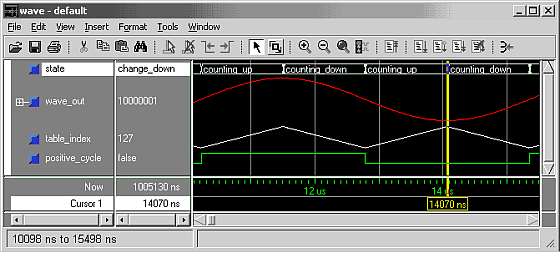
Synthesis
Most synthesis tools recognize the case statement in function get_table_value as a ROM.



